Glossary of Terms
A
Aggregating Meter
A type of Kaizen Energy virtual meter that sums the output of its sub-meters (child meters). Example: Aggregating Meter A has two sub-meters B and C with their corresponding consumption values. The output of A = B + C.
AHU
Air Handler Unit which heats and/or cools air.
Alert (CopperTree)
An email message sent automatically on the occurrence of a new Insight. The user needs to be subscribed to the insight in order to receive the alert.
API
Application Programming Interface – A set of rules that dictates how software components interact with each other.
B
BACnet (HVAC)
Building Automation and Control network – A communications protocol for building automation and control networks. BACnet is used for controlling the systems within a building, such as heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) as well as lighting, access, and fire detection systems. BACnet is a set of rules that machinery uses to exchange data over a computer network, capable of controlling systems based on their function, rather than physical design. (Source: BACnet.org, “BACnet: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions”)
Balance Point (HVAC)
The outdoor temperature above which the building does not require heating.
BAS
Building Automation System (a.k.a. BMS: Building Management System; EMS: Energy Management System; EMCS: Energy Management Control System) – A system designed to control building equipment and its operations. It controls the temperature, relative humidity, pressure, etc. within the building, monitors the operation, and report failures.
Base Temperature (HVAC)
The ideal indoor temperature, which is also the reference temperature given in the definition for degree day.
Base Load
The constant, temperature-independent energy demand of a building. Commonly this includes lights and computers.
Baseline
Representation of standard energy performance used for comparative purposes.
Baseline Formula (HVAC)
Formulas describing the relationship between energy consumption and selected variables are sometimes used to estimate the energy baseline. Statistical sampling techniques (such as regression analysis) can be used to derive such formulas.
Benchmarking
Building energy benchmarking is the ongoing review of your organization’s energy consumption to determine if your building’s energy performance is getting better or worse in comparison to itself, other buildings in your portfolio, and/or its peers. (Source: Natural Resources Canada)
Binary (computer)
A data type which can take only two possible values. (HVAC) Often used to store Fan Status (Off/On), Valve, Damper and Door position (Closed/Open), Logic States (No/Yes).
BLR
Kaizen tag for Boilers.
C
CCV
Kaizen tag for Cooling Coil Valves.
CDD (HVAC)
Cooling Degree Day – A measure of how much (in degrees), and for how long (in days), outside air temperature was higher than a specific balance point temperature (or base temperature). CDDs are designed to reflect the demand for energy needed to cool a building. Here is the source.
Chart
A graphical representation of information. Kaizen provides a selection of Charts in the Community Library that you can use to display useful information. Charts can be added to a building using the Chart icon.
Chart Template
A predefined graphic with internally applied parameters. A Working Chart can be created from a Chart Template once it has been downloaded into the building. A template is a framework for your Working Chart which is created when you add real inputs to the template.
CHLR
Kaizen tag for Chillers.
CHW or CHWS
Chilled Water System- A system that runs water through coils, pumps, etc. so that it absorbs heat thereby providing cooling, and then returns the water to a chiller, heat pump, or other heat-rejecting equipment where it is cooled.
CHWST
Kaizen tag referring to Chilled Water Supply Temperature
Cloud (computer)
Computer resources are delivered over a network (typically the internet). (Source: PCmag )
Coefficient (mathematics/statistics)
A constant value multiplies a variable by its value. For example, in the following formula, ‘
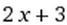
‘2’ is the coefficient in front of the variable ‘x’. This means that every value of x in the formula is multiplied by 2. Similarly, the coefficient doesn’t have to be a number but can be a letter, representing an unknown, unchanging number. For instance in
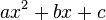
‘a’ and ‘b’, are coefficients, and the letter ‘c’ represents a constant value. (Source: Wolfram Alpha)
Community Library
A repository to find Rule Templates and Chart Templates that can be used in a building. CopperTree provides a set of published Rule Templates. Users can add custom Rule Templates to the Community Library.
Consumption (energy)
The amount of energy consumed in a process or system, or by an organization or society.
Container (generic)
Some abstract objects for grouping of items or other containers. The containers could be presented as a tree. The container could be used for the architectural view (floor1, floor 2, etc), for system view (boiler, chiller), or any other kind of view.
CoV
Change of value – a Trend Log set to CoV will only collect data when the tracked value is more than a threshold away from the last recorded value. The other option is a ‘polled’ trend log.
CSV (computer file format)
Comma-separated values – CSV files store tabular data (numbers and text) in plain-text format. A CSV file may consist of any number of lines, separated by line breaks. Each record consists of fields, separated by some other character or string, most commonly a literal comma or tab. Usually, all records have an identical sequence of fields. (Source: data.okfn.org)
CTL
Calculated Trend Log – a trend log that has been calculated from existing data. Once it is calculated, it is used in an identical method to BACnet Trendlog.
CopperCube
The hardware component of the CopperTree solution gathers data from your BAS network. Manufactured by Delta Controls, CopperCube is the site-level element of CopperTree’s product system. This native BACnet® device searches your BAS network to locate all BACnet trend logs (but not from points) and archives those trends in its internal database providing redundant and long-term storage of your building’s information. The data it collects is sent AMQP to central storage servers in CopperTree Analytics’ data center, where it is analyzed by Kaizen.
D
Deliverable (generic)
A tangible or intangible object, such as a report, document, notification, or dashboard intended to be delivered to a customer.
Demand
The rate of energy use by a particular building system. Demand is most often measured in kW or BTU/Hr.
Device (BACnet)
Devices are your building controllers with input and output capabilities. These building controllers monitor and control building equipment operations.
Device range (BACnet)
The range of controllers in a building. Building controllers are assigned unique numbers that differentiate them from the remaining controllers in the same building, thereby allowing communication between devices.
E
End-user
The person who works with the equipment installed in the specific location. It could be the facility manager or other staff involved in the building monitoring.
Energy Insight
A type of insight from the ‘Energy KPI’ perspective. Raises a flag when energy consumption exceeds a target threshold.
Energy Management Information System (EMIS)
A performance management system that enables individuals and organizations to plan, make decisions, and take effective action to manage energy use and costs. For more information, please visit Natural Resources Canada.
Energy Meter
See definition for Meter.
ERV
Kaizen tag for Energy Recovery Ventilators.
Energy Usage Intensity (energy)
A building’s EUI is calculated by taking the total energy consumed in one year (measured in kBtu) and dividing it by the total floor space of the building. For more information, please visit Natural Resources Canada online at: nrcan.ga.ca and ENERGY STAR.
Event (BACnet)
Refers to the BACnet® event (EV) object. CopperTree uses this word in the same way Delta Controls uses it.
Event-Driven
Refers to a task such as texting an alert message initiated by an event such as the energy consumption surpassing the energy baseline.
F
Fault
Any problem that has occurred with equipment as a consequence of the improper use or malfunction of equipment, devices, sensors, and other parts involved in the building automation system.
Fault Detection Insight
A type of insight from the ‘Equipment Operation’ perspective. Sends an insight when equipment is deemed to be performing poorly/malfunctioning.
FCE
Kaizen tag for a Final Control Element.
G
Golden Standard
A snapshot or blueprint of the building control system. Any deviation from that snapshot becomes an insight. This building snapshot consists of most of the standard BACnet objects and their relevant properties. Kaizen takes the first set of object’s property values received for each building and makes it the golden standard. The snapshot of an object’s property values is deemed as the ‘standard’ for all future comparisons with the current values. A Golden Standard Insight is raised when a BACnet object is found to be different from its golden standard ‘snapshot’.
Golden Standard Insight
A type of insight based on Golden Standard change.
GUI
Graphical User Interface – a visual way to communicate/control an electronic/digital device. Kaizen has both a GUI for Users and an API for other applications such as entelliWEB
H
HCV
Kaizen tag for a Heating Coil Valve.
HDD
Heating Degree Day – a measure of how much (in degrees), and for how long (in days), outside air temperature was lower than a specific balance point temperature (or base temperature). HDDs are designed to reflect the demand for energy needed to heat a building. Source: degreedays.net
I
Infrastructure
A type of insight that focuses on an issue, fault, or event in a building related to its control system operation or data collection infrastructure. They are enabled by default when a new building is created.
Insight (CopperTree)
An issue, problem, fault, condition, or note-worthy event identified by Kaizen’s analytical engines needs to be brought to the user’s attention.
Insight Priority
A way to evaluate insights based on importance, monetary value, and/or urgency. The following priority categories are available: Default Priority (Low, Medium, and High), Potential Cost Savings, Energy Impact, Comfort Impact, Environmental Impact, Property Impact, Safety Impact, Urgency Score, Heating Impact, Cooling Impact, and Ventilation Impact. For a definition of each category, refer to the Insight Prioritization page.
Insight Type
A way to categorize insights. Insight types are used to filter, setup subscriptions, and generate insight reports. There are several options, including energy, energy KPI, fault detection, golden standard, infrastructure, and integrity KPI.
Integrity KPI Insight
A type of insight that focuses on a performance issue from the ‘Operational Performance’ perspective.
Issue
The generic term is used to describe the output of the analysis engine. Issues are of different types and are determined by the analysis types that the engine is running.
J
K
Kaizen
In the Japanese language, Kai means ‘good’, and Zen means ‘change’. CopperTree’s Kaizen is a SaaS platform that analyzes building data and empowers users to make ‘good changes’ needed to continuously improve building performance.
KPI
Key Performance Indicator – a type of performance measurement that evaluates if the intended outcome or goal has been achieved. This metric gives information on how close – or how far – what has been achieved is from the agreed-upon success level. For example, a VAV system with a KPI of 70 out of a success score of 100 means that for 70 samples out of 100, the space temperature was within the desired setpoint.
L
Location (CopperTree)
A Coppertree logical concept to describe a subset of a site by means of a set of device number ranges. (e.g. device 100..199, 2000..3999). Multiple device ranges may be used to completely describe the location. Locations are commonly used to describe the individual buildings within a campus-wide site.
Location ID
Kaizen assigns a unique building ID named for every building added so that the information collected from the buildings through CopperCube will populate the correct locations in the database.
Logic Block
The fundamental building element forms a logic flow. There are three types of logic blocks:
- Input Blocks: Provide input e.g., weather data, trend logs
- Function Blocks: Process 1 or more inputs and generate 1 output
- Output Blocks: Output the data for storage i.e. Calculated Trend Logs
Logic Builder
The tool is used to create logic flows and logic rules. The term Logic Editor may also be used.
Logic Flow
A set of connected logic blocks that process trend logs into Insights and/or calculated trend logs.
Logic Rule
A collection of all the logic flows is viewable in the logic builder. Also called a rule template.
M
MAD
Kaizen tag for a Mixed Air Damper.
Meter
A device used on utility mains or feeds to measure resource consumption and rate of consumption (a.k.a demand). Resources include electricity, gas, water, and heat content. Also called an Energy Meter.
MUA
Kaizen tag for a Make-up Air unit.
MT
See “MultiTrend”.
MultiTrend (Delta Controls)
Also called Multi-Trend, Multi Trend, and MT. A compilation of trend logs that allows easy comparison.
N
Network connection types
When CopperCube is installed in a building, it needs to communicate with other devices in the network. There are three network connection types by which a CopperCube can communicate with other devices in your network. These connections can be made through a direct Ethernet connection, a regular IP connection, or a foreign IP connection. A CopperCube can also connect with one or more networks at the same time.
O
P
Polling
A polling Trend Log collects data at consistent user-defined intervals (every 15 minutes, once a day, etc). The other option is a ‘CoV’ Trend Log.
Q
R
Report
A snapshot of information at a particular point in time for a particular period of time. Kaizen can create Reports that render processed data into a visual format such as a graph or table. Reports are scheduled to be run and delivered via email to users or groups who have subscriptions to the report.
- Reports can be run on demand.
- Reports can be scheduled to run at a specific time schedule on a recurring basis; see subscription.
RTU
Roof Top Unit – an Air Handler Unit which heats and/or cools air located on the roof of a building.
Rule Template
A logic template that contains the Logic Flow and allows users to set parameters such as Insight type, trigger block, trigger type, and aggregation interval.The template from which Working Rules are created. Users can download Rule Templates into their building from the Community Library, copy from an existing Template or create them from scratch.
S
SaaS
Software as a Service – a software delivery model in which software and associated data are centrally hosted on the cloud. Sometimes referred to as “on demand” software.
Schedule-driven
Refers to a task such as automatic report delivery via email initiated by a schedule where the exact date and time are defined.
Site (CopperTree)
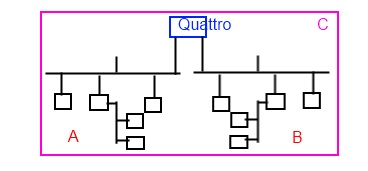
A SET of BACnet devices that may communicate using only BACnet protocol. The devices are uniquely numbered within the SET. The SET may contain one or more interconnected BACnet networks (i.e. an Ethernet backbone & several mstp networks). Graphically a SITE is depicted as:
- Two examples of a SITE:
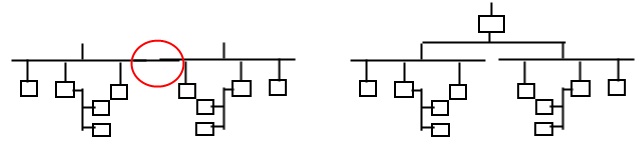
Below is a diagram which is NOT an example of a SITE; since the devices on A cannot communicate with the devices on B. This is TWO SITES: - Not a site – but rather this is 2 separate sites.:
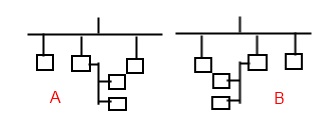
Be aware: Delta partners and Delta/CopperTree customers often use ‘site’ to describe a collection of BACnet devices belonging to a given client (i.e. City of Edmonton) or which are geographically co-located (i.e. SFU campus) as a site. But this is often incorrect as the collection of devices does not meet the strict definition of SITE – i.e. not all the devices can ‘see’ (communicate) with each other. - Quattro uses the above definition of SITE. Quattro is MULTI-SITE capable, since it may communicate with multiple SITES simultaneously. However, the SUPERSET collection of devices created by Quattro’s multi-site capability does NOT make the SUPERSET a SITE. E.g: The collection [C] is NOT a SITE. It remains multiple distinct SITES [A] and [B].
- Quattro as a Multi-SITE (SUPERSET):
Subscription
An automatic method to receive alerts from Kaizen, including event-based Alerts advising of changes to a system and periodic reports that deliver summarized information by email.
SSP
Kaizen tag for Supply Static Pressure
System (Kaizen)
A structured perspective that allows users to organize and represent equipment in their building as a collection of building systems. Kaizen Systems also allows a new workflow to create multiple Working Rules simultaneously on similar pieces of equipment.
T
Tag
Kaizen Systems adds a tagging model to allow descriptive data within Kaizen. Tags are simple keywords or terms assigned to a piece of information (such as a BACnet object) and are used to categorize the content. The list of tags available in Kaizen comes from the tags listed and defined by Project Haystack.
Template
See Chart Template or Rule Template.
Trend Log (BACnet)
Also called a TrendLog or TL. A BACnet object that collects data in the form of time-value pairs from a specific monitored object (eg, schedule, analog input, binary variable, etc.). These values can be captured at either regular polling intervals or on a Change of Value (CoV) of the monitored object property. When the time interval passes, or a Change of Value occurs, a log is produced with the property value and a date/time stamp which is placed into a buffer for future retrieval. This buffer can be optionally fixed in size by the user. Trend Log data is used in Kaizen for many types of analytics. ( Source)
Trigger Block
A binary output logic block that can be used to trigger when insight has been detected.
Trigger Type
Determines what kind of data will trigger an Insight. These are the trigger types available in Kaizen Logic Builder: Rising Edge (transition from low to high), Falling Edge (transition from high to low), Falling and Rising (both transitions), and Active High (anytime value = 1).
Type of equipment
When creating a System, the type of equipment should be included to allow auto-detection of applicable Rule Templates. There are several predefined types of equipment tags, stored as a string value.
U
UV
Unit ventilators are unitary heating/cooling assets which have direct access to outside fresh air.
V
VAV
Variable Air Volume – a type of HVAC system, where building temperature is controlled by a system of air ducts. Also, the colloquial term used for the terminal boxes within a variable air volume system. The terminal boxes contain a control damper is often equipped with a reheat coil.
Variance Meter
A type of Virtual Meter that gives the difference between the parent meter and the sum of the other sub-meters.
VFD
Kaizen tag for Variable Frequency Drives.
W
Widget
A graphic component placed on a GUI dashboard that displays information and allows users to interact with its content in a number of ways.
Working Rule
A rule template with the following applied parameters: priority, TL(s) to be used as a data source for the input blocks, and an insight message.
Working Chart
A working chart is a chart template with user applied parameters: e.g., specific Trend Log objects or default date range.